Breadcrumb
Interpreting the Pressure Waveform
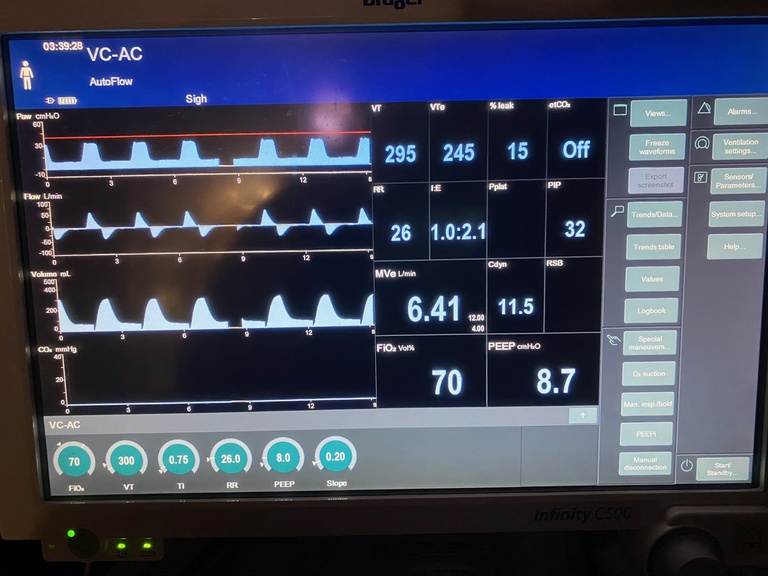
The pressure waveform is usually the topmost waveform displayed on the ventilator. From it can be obtained information regarding the pressure in the circuit, including the peak and plateau pressures.
The plateau pressure is a measure of alveolar pressure. It can be obtained by performing an inspiratory hold, which causes air pressure in the circuit to equilibrate, removing the pressure contributed by airway resistance. A "normal" plateau pressure is less 30 cm H20; elevation beyond that indicates poor lung compliance, such as can be seen with pulmonary edema, ARDS, pneumothorax, pleural effusions etc.
The peak pressure, seen on the top right hand corner of the screen, represents the total pressure in the circuit: that is, the sum of the plateau pressure and the airway pressure (Peak Pressure = Plateau Pressure + Airway Pressure). A normal peak pressure is less than 40 cm H2O. Causes of elevated pressure can be either an elevation in the plateau pressure or an elevation in resistance. To determine where the issue is an inspiratory hold can be used: if the plateau pressure is normal (that is, less than 25-30 cmH20) then consider issues that would cause increased airway resistance, such as bronchospasm, mucous plugging and a kinked endotracheal tube.