Breadcrumb
Interpreting the Flow Waveform
Square inspiratory flow waveforms are seen in volume control modes of ventilation, as the ventilator is delivering a constant flow of air to meet its pre-specified goal volume. This is in contrast to pressure control modes of ventilation, where the flow waveform is decelerating, as the ventilator needs to deliver progressively less air to maintain a given pressure.
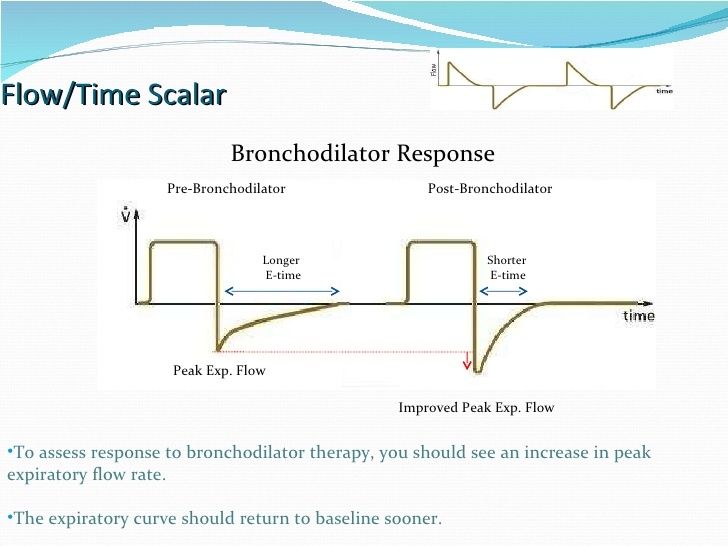
The expiratory part of the flow waveform can reveal a prolonged expiratory phase, which can indicate airway obstruction (e.g., from an asthma exacerbation).
The flow waveform can also reveal gas trapping; when the expiratory flow fails to return to baseline, before the beginning of the next breath, it indicates that exhalation did not finish before the next breath began, which can lead to accumulation of gas in the alveoli.